With the rapid rise of artificial intelligence (AI), many industries have undergone a massive transformation — and the world of localization is no exception. More and more developers and publishers are opting to cut costs on products by replacing human translators with neural networks.
Today, AI-powered translation tools like Google Translate, DeepL, and other neural machine systems can instantly render texts on virtually any topic. Fast, convenient, and widely accessible — what’s not to love? But while these tools are impressive, they still can’t fully replace the expertise of a professional linguist. In this article, we’ll dive headlong into when machine translation is a helpful ally — and when the human touch is absolutely essential.
When is AI translation a good fit?
There’s no denying it: AI translation can save both time and money. But speed isn’t everything. Dig a little deeper, and you’ll find that faster doesn’t always mean better. In fact, machine translation can hurt your content if misused — especially with highly specialized or literary texts that demand cultural nuances and careful adaptation.
AI-powered translation tools excel in the following situations:
Basic understanding of a text. When you need to quickly grasp the general meaning of a document, news article, or email, machine translation does the job quite well. It’s perfect for personal use, travel, or a quick overview of foreign materials.
Technical translations with repetitive phrases. In manuals, guides, user instructions, and code, you’ll often find standardized expressions that AI can handle accurately and efficiently. These types of texts rarely require creativity, making machine translation an incredibly effective tool.
Automated business translations. Many companies rely on AI to translate internal documents, reports, and corporate communications. In these cases, speed is crucial for processing large amounts of information, and any mistakes can be corrected by in-house staff when necessary.
Real-time news and article translations. Many media outlets use AI for rapid translation and the distribution of information. This is particularly valuable when speed is more important than perfect accuracy, such as in breaking news situations.
Chats and informal communication. Whether in messengers, forums, or comment sections, AI enables the quick translation of messages in real time. While the quality may not be perfect, it keeps the conversation flowing. No messenger or forum is willing to pay real translators to adapt jokes or memes in casual exchanges.
Translating large volumes of text under tight deadlines. When hundreds of pages of documentation or a website need to be translated, AI speeds up the process considerably. After the initial translation, an editor can refine and improve the quality of the text.
Automated subtitle and video translations. Many video platforms use machine translation to generate subtitles, instantly reaching an audience across different languages. While these translations often need editing, they simplify content accessibility greatly.
As you can see, AI works best when there’s no need for creative input or deep expertise in a highly specialized field. If you need to translate a large volume of technical text in a short amount of time, with no expectations for high artistic quality, AI is the perfect choice.
When is a human translation necessary?
Despite the impressive advances in AI, there are areas where only a professional translator can truly deliver:
- Creative texts. Novels, poetry, screenplays — these require more than just word-for-word translation. They demand the conveyance of style, emotion, and cultural nuances. AI simply can’t match that level of artistry yet.
- Legal documents and contracts. Contracts, court rulings, laws — these texts are packed with specialized terminology where even the smallest error could lead to serious legal ramifications. Precision here is paramount.
- Marketing and advertising materials. Texts aimed at engaging an audience need a creative approach, cultural adaptation, and emotional appeal. This is a realm where AI is still far from capturing the full depth of human insight.
- Medical translations. In medical reports and instructions, a mistranslation could endanger lives. This field demands absolute accuracy and specialized knowledge of complex terminology.
- Diplomatic and official documents. The subtleties of language and the political undertones in official negotiations require a professional touch. Context and consequences matter — every word is important and could influence the future of diplomatic relations between the parties.
Despite the extraordinary strides made in neural network development, we can never overlook the human factor. When it comes to artistic, stylistic, and cultural adaptation, or the need to maintain a rigorous terminological foundation, only a skilled human translator can truly get the job done.
AI vs. human translation: pros and cons
| Criteria | AI Translation | Human Translation |
| Speed | Instantaneous | Takes time |
| Accuracy | High for technical texts, low for creative ones | Consistently high across all types of content |
| Cost | Low or even free | Higher, varies by complexity |
| Flexibility | Limited, lacks cultural awareness | Highly adaptive, context-aware |
| Emotional Expression | Absent | Captures tone, style, and cultural subtleties |
What is MTPE?
MTPE (Machine Translation Post-Editing) is the process of refining machine-translated text with a human touch to boost its quality. If you’re looking to cut localization costs and ride the wave of neural networks, skipping the post-editing step is a risky move. AI can help you save time, but it’s human editing that ensures the final result meets your quality output standards.
At first glance, the combo of AI and MTPE might seem like the perfect solution — faster, cheaper, and still competitive in quality. But even this approach has its limits. For content packed with niche terminology or requiring a creative adaptation of humor and cultural nuances, it’s best to bring in the pros. Right now, AI just doesn’t cut it in these areas. In fact, fixing some AI-translated texts takes more effort than translating them from scratch.
That said, if you’re dealing with large volumes of technical text, AI can definitely speed things up. The machine handles repetitive, template-style content with ease, while a human editor or translator polishes up any rough edges.
And what about game localization?
Game texts come in all shapes and sizes — UI strings, dialogues, quests, item descriptions, marketing blurbs, and more. Each one calls for a tailored approach. On top of that, games themselves can be highly specialized. Say your game’s about rugby — your translator better know the lingo and have a solid grasp of the sport. If it’s a story-rich game, then cultural adaptation becomes critical. You’ll need to localize with sensitivity to regional traditions, social norms, and even religious contexts.
In practice, even translating a game menu is no simple task. For instance, the same game might have vastly different interface localizations across consoles — right down to how the word “button” is translated. Here, deciphering string IDs becomes crucial — they often hold clues about the platform, helping ensure players see the correct control prompts and aren’t suddenly told to press squares and circles on an Xbox controller.
But one of the biggest keys to successful game localization is context. And not even a native-speaking professional can do the job right without it. That’s why relying solely on AI tools for game translation just doesn’t get the job done. Take Chicken Road, for example — its absurdist humor and regional references required deep cultural adaptation to truly resonate with players worldwide. If nothing else, make sure you leave time for at least some MTPE. If nothing else, make sure you leave time for at least some MTPE.
When it’s smart to use AI in game localization:
1. Speedy UI translations. AI is great for quickly translating short in-game text elements like menus, item names, or settings. But — and this is key — it must be followed by a human review. Why? Because AI often misses the nuances of context, especially when dealing with ambiguous terms.
Take German, for instance. It typically uses the infinitive form of verbs for UI buttons. One common AI slip-up? Defaulting to formal address with “Sie” instead of the more appropriate structure.
Here’s what that looks like in practice:
![]()
This is where a human editor needs to step in: they won’t miss a detail like this and will fix it to Bestätigen — the correct form meaning “to confirm,” not “confirm it.”
Quests are another pain point. They often require the informal imperative form — something machine translation rarely gets right. Like this:

What it should be: Erreiche (“Choose” or “Place” using the friendly, informal “du” form). This kind of mistake happens when you drop English text into DeepL and copy-paste the result without checking. It’s the most common localization error in German.
2. First-draft translations of game descriptions. Machine translation can churn through large volumes of text fast, but you’ll still need a human touch. Consistency in terminology is critical, and AI isn’t always reliable here.
Say you’re translating the word level. In German, it’s Level when referring to game stages, but Stufe might apply in other contexts. If the AI flips between the two without context, you end up with a dreaded inconsistency — a major style and quality issue. In fact, using Stufe instead of Level to mean anything other than the upgrade level of a particular object is a clear-cut mistranslation.
3. Localization patches and updates. If patches drop every week, speed is everything. AI can help localize new game elements quickly.
4. Player feedback and comments. Want to know what players think in real time? AI can auto-translate player reviews and comments across languages, making it easier to gather global feedback fast.
When you need a human translation:
1. Capturing humor, slang, and cultural references. Let’s face it: AI just isn’t funny. It might try to translate a joke, but only a professional human translator can truly make it land. Humor relies on local flavor, wordplay, and cultural context.
Case in point when a human is needed:

In the original English text, the character cleverly rhymes date with eight, but when translated literally by AI, that rhyme gets completely lost. The result? Nicht—acht. Not quite the same punch, right? This is where creativity steps in.
Take this line: “Tom, don’t forget the date — it’s nine, two, and eight!” AI rendered it in German as: “Tom, vergiss das Datum nicht – es sind Neun, Zwei und Acht.”
Enter the human translator: “Tom, vergiss das Datum nicht – es sind Neun, Zwei und Acht, so wie’s im Buche steht und kracht!”
The translator brought in a rhyme, kracht and acht, preserving the original rhythm and poetic feel. Why does it matter? Because this isn’t just a cute rhyme — it’s a child’s verse containing the code to a safe, a pivotal clue in the game’s quest. Sure, the second part had to be tweaked a little to make the rhyme work. But the meaning? Still spot-on.
Or another example: joke translations. Here’s how a professional linguist adapted one for a German-speaking audience:
English:
Why don’t skeletons fight each other?
Because they don’t have the guts!
In the original English joke, the pun hinges on the word guts, which has two meanings: literally (internal organs) and figuratively (courage or bravery).
Here’s how a professional linguist translated this pun into German:
Warum kämpfen Skelette nie gegeneinander?
Weil ihnen der Mumm fehlt!
The German version cleverly preserves the pun through the word Mumm, which also carries a double meaning. While not literally referring to guts, Mumm implies both courage and, in a figurative sense, something inside, evoking that same playful twist. For German speakers, it lands as a witty, culturally resonant play on words, just like the original.
Now let’s see how AI handled that task. We trimmed the joke a bit and let the “machine” take a crack at it.

When translating word-for-word from English into German, the term Mumm (akin to guts) sticks around, but pair it with the verb haben (to have), and the meaning gets lost. What you’re left with is a literal translation that completely misses the punchline.
2. For dialogue and storytelling. Natural, believable dialogue is what breathes life into a game’s world. But AI? It tends to oversimplify, generalize, and strip away emotional nuance. In translations, it focuses on the gist, not the core, and is likely to overlook important details. When characters are in love, in pain, or in conflict, their words need to feel real. That’s not something you can automate. The natural sound of the language comes to the fore here. You need a human ear, a human heart.
The most iconic meme of them all? Machine translations from Chinese. Earlier, we showed examples using the English-German language pair. Since both languages come from the same family — Germanic — the localization process can be relatively smooth. But Chinese? That’s a whole different beast. With its logographic (character) writing system, Chinese throws a serious curveball at neural machine translation. The result? Raw AI-translated texts that are often downright unusable without serious human intervention.
Below is an example of how a Chinese game was translated using AI. The first column contains the original text, the second one contains the AI translation, and the last is the version polished by a human translator.

Example of AI-powered Chinese translation and editing
In Chinese, even the smallest detail can completely alter the meaning of a statement. This presents a challenge for AI, as the logographic writing system is incredibly difficult to interpret. In the following examples, we’re dealing with mistranslations: words and terms have been translated incorrectly.
In the first instance, we get “crowbar” instead of “claw hammer,” and in the second, “plate” instead of “blister” (as in a pill blister pack), while in the third example, the AI, instead of translating “writing on the mirror,” practically made the mirror itself the author of the text on it. The source text was too complicated for the AI, and the editor made it more readable. AI loses the meaning embedded in the original text. Its biggest flaw is its overly literal translation. And when it comes to characters, the problem only deepens.
Marketing materials. Game descriptions, advertising campaigns, and slogans all require a creative approach. AI lacks imagination and works strictly within a precise system of algorithms, leaving it devoid of the creative potential that’s crucial for marketing, where the main goal is to captivate an audience. One key feature of such materials is conciseness. A translator always faces the tough task of conveying the core message succinctly.
Here’s a prime example of marketing text.
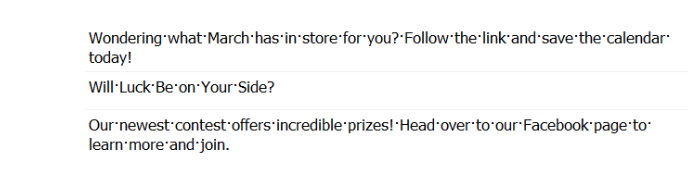
In the English version, we see the line “Will Luck Be on Your Side?” (akin to the meaning “Will luck smile upon you?”). If you translate it into German using AI, the result will sound unnatural.

Marketing texts demand brevity and impact, but German can be quite cumbersome due to its complex grammatical structures — you can’t simply eliminate elements to shorten a sentence or phrase. Moreover, when using AI for German translation, it tends to default to a formal tone, as that’s its standard setting.
A real human translator, however, can bring your text to life, making it vibrant and captivating.
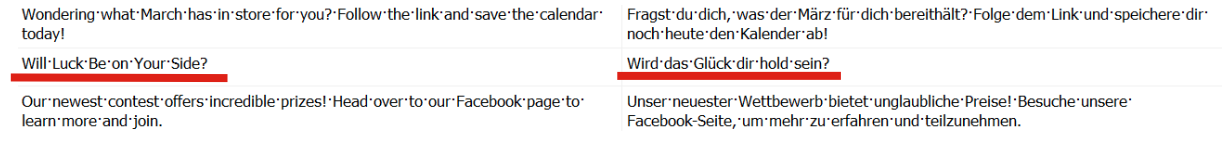
The linguist chose the phrase “Will luck accompany you?” It sounds more natural to native speakers and effectively conveys the core message.
What conclusions can we draw?
AI has already become an essential tool and ally for localization professionals, helping to simplify and speed up the process. However, relying on it entirely is not the best approach. The work of skilled linguists is still critical, as AI is incapable of capturing every nuance like context, humor, and cultural elements.
Of course, the choice is always yours, but it’s important to base it on your objectives, content type, and the level of accuracy required. Remember, AI is not a cure-all or one-size-fits-all solution. Strive for balance, use MTPE (Machine Translation Post-Editing) wisely, or entrust the work to professional translators to achieve the quality that perfectly fits your needs.